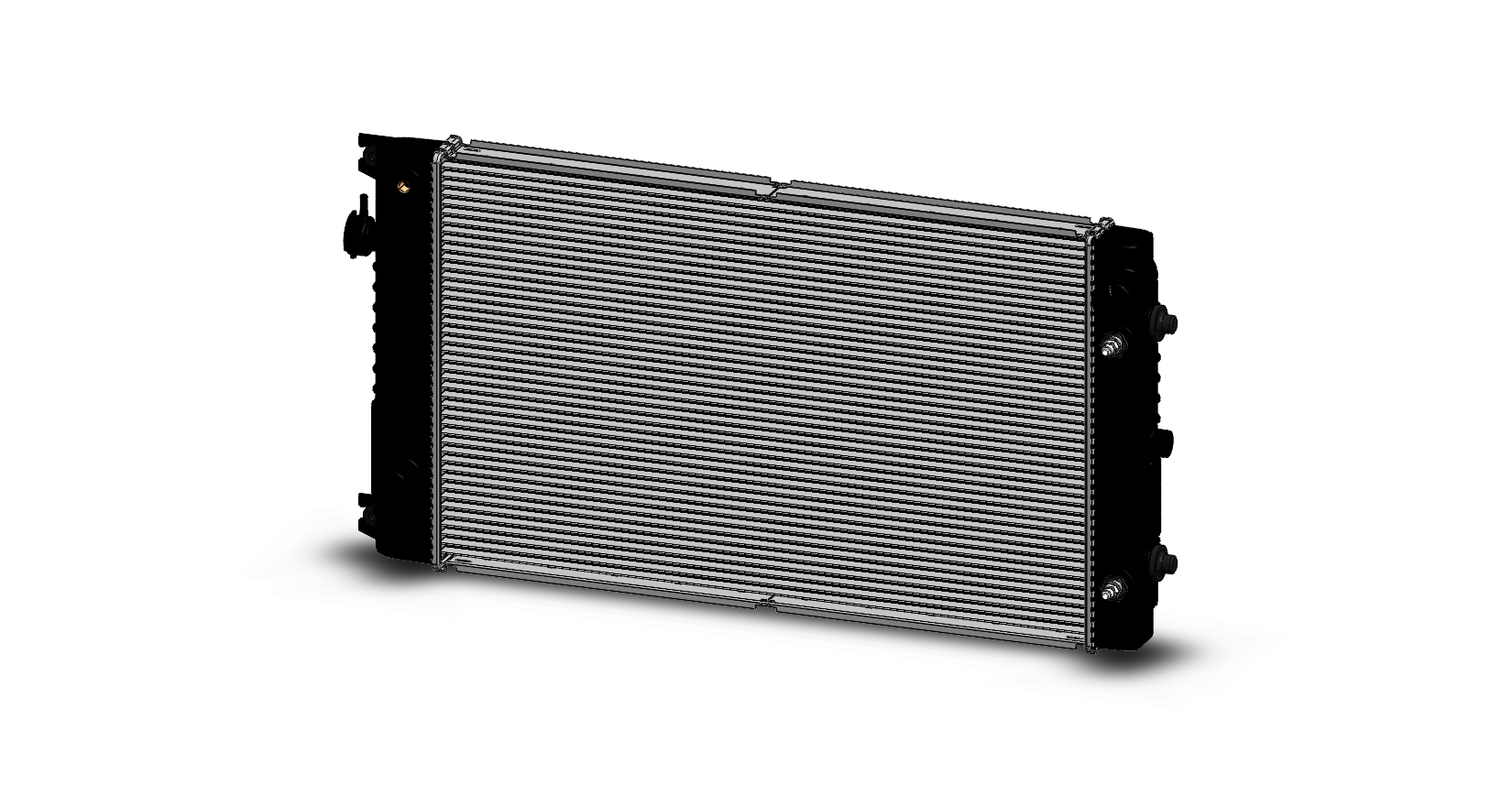
Tube & Header Radiator
- Application: On-Road & Off-Road Specialty, Power Generation
- :
A Radiator-tube is a key component of a radiator, which is an essential part of a cooling system used in various applications, including automotive vehicles, industrial machinery, and power generation equipment. Here’s a summary of Radiator-tubes:
- Construction:
- Radiator-tubes are typically made of metal, commonly aluminum or copper, due to their excellent thermal conductivity and durability.
- These tubes are designed to circulate the coolant (usually water or a water/antifreeze mixture) through the radiator, allowing for heat exchange with the surrounding air.
- Functionality:
- Radiator-tubes play a crucial role in the heat transfer process within the radiator. As coolant flows through these tubes, heat absorbed from the engine or other components is transferred to the tube walls.
- The large surface area of the tubes facilitates efficient heat dissipation, allowing the coolant to release heat to the surrounding air as it passes through the radiator.
- Heat Exchange:
- Heat exchange occurs as the coolant absorbs heat from the engine and other hot components, raising its temperature.
- As the hot coolant flows through the Radiator-tubes, heat is transferred to the tube walls, and then to the surrounding air through convection.
- As a result, the coolant temperature decreases, and the cooled coolant is circulated back to the engine or other components to absorb more heat, completing the cooling cycle.
- Efficiency and Performance:
- The design and construction of Radiator-tubes are optimized for efficient heat transfer, ensuring effective cooling of the engine or other systems.
- Their configuration maximizes the surface area available for heat exchange, allowing for rapid cooling and maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
- Radiator-tubes are often engineered to withstand high temperatures and pressures, ensuring reliable performance even in demanding conditions.
- Applications:
- Radiator-tubes are used in a wide range of applications where cooling is required, including automotive vehicles (cars, trucks, buses), industrial machinery (generators, compressors), and power generation equipment (stationary gensets, mobile gensets).
- They are integral components of radiator assemblies, working in conjunction with other components such as fins, tanks, and headers to facilitate efficient heat dissipation.
- Maintenance and Care:
- Regular maintenance of Radiator-tubes is essential to ensure optimal cooling system performance.
- This includes inspecting for leaks or damage, cleaning debris and buildup from the tubes and fins, and ensuring proper coolant levels and quality.
In summary, Radiator-tubes are fundamental components of radiators used in cooling systems for various applications. Their efficient heat transfer capabilities, durability, and versatility make them vital for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and ensuring the reliability and performance of engines and other systems.